“It’s hard to beat a person who never gives up.” – Babe Ruth
Present Continuous Tense (Simplified)

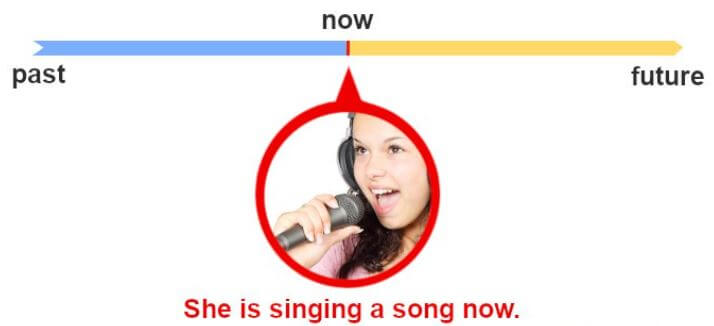
The present continuous (also called the present progressive) tense indicates that an action has already started in the past and it’s still going on, and may continue into the future. Let’s look at the image below to understand more.
Improve Your English Grammar: Fix the Top 14 Grammar Mistakes
In the above picture, the girl started singing in the past and she is still singing, and this action of singing will continue in future.
Let’s understand this with another example:
You’re in a restaurant. The waiter has served the food.
You’re eating now. Now you get a call from your boss. You will say that, you’re eating now.
You already started eating before the call came and you may or may not eat after you end the call, but you haven’t finished eating yet.
The Formula for present continuous:
S = Subject (I, he, she, it, you, we, they)
I am (I’m)
He/she/it is (He’s/She’s/It’s)
You/we/they are (You’re/We’re/They’re)
V = Verb
Eat (+ing) = Eating
- Positive: S + (is/am/are) + v (+ing).
I am eating. She is eating. You are reading a book.
- Negative: S + (is/am/are) + not+ v (+ing).
I’m not crying. He’s not running. They’re not running.
- Question: (Is/am/are) + s + v (+ing)?
Am I drinking? Are you sleeping? Is it dead?
- Negative question: (Is/am/are) + s + not + v (+ing)?
Am I not writing? Are we not going? Is she not dancing?
Present Continuous Tense Quizzes and Exercise:
Watch this video before the quiz:
Write questions. Use the present continuous.
- Who’s laughing? (who / laugh?)
- (why / he / go?)
- (she / eat / rice?)
- (what / they / do / in Dubai?)
- (what / he / write?)
Fill in the blanks:
- Kayla and Paul have had an argument and now (they / speak) to one another.
- The situation was very good but now (it / get) worse.
- Brian isn’t singing (sing) today. He isn’t (feel) very good.
- (They / look) for Maria. Do you know where she is?
- The computer has been repaired. (It / work) now.